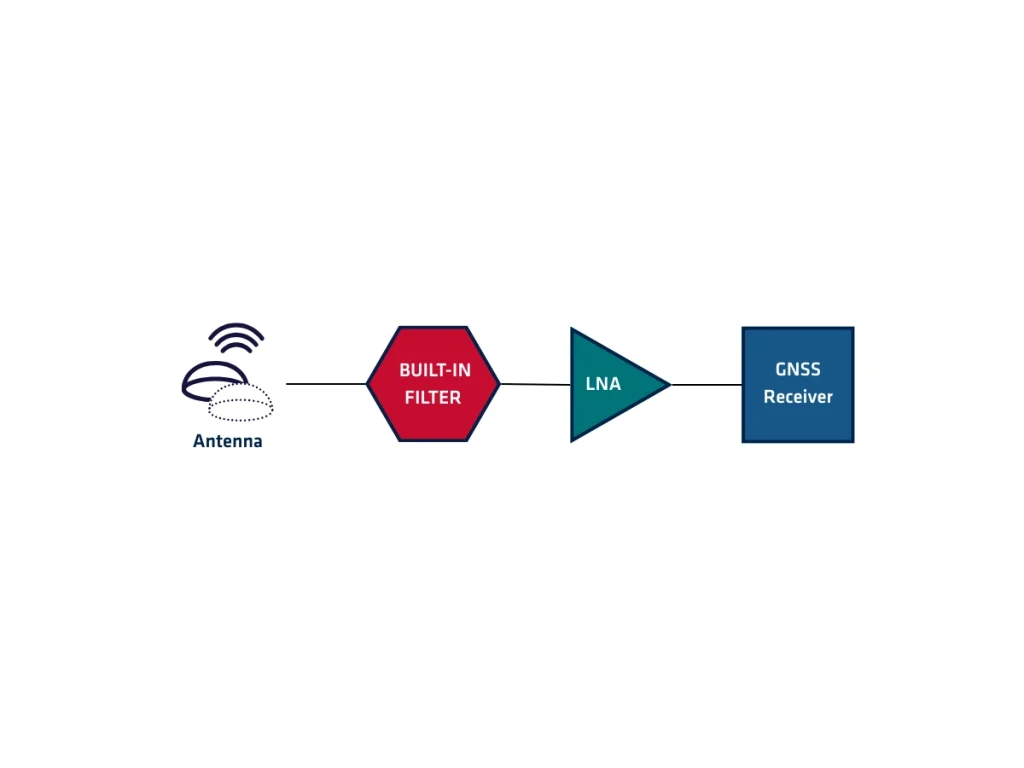
Built-in filters in GNSS antennas play a vital role in protecting the receiver from unwanted signals and improving overall system performance. These filters block out-of-band interference while allowing GNSS frequencies to pass through with minimal loss.
First, GNSS signals are extremely weak when received at the antenna. Any nearby strong signals, such as cellular, radio, or TV transmissions, can easily overpower them. Built-in filters prevent these unwanted signals from reaching the low-noise amplifier and receiver.
Next, bandpass filters are the most common type used in GNSS antennas. They allow only specific frequency ranges—such as GPS L1, L2, or L5 bands—to pass through. This selective filtering improves signal clarity and reduces noise. Additionally, filters reduce the risk of receiver desensitization. When strong out-of-band signals enter the system, they can degrade sensitivity. Filters help maintain a clean signal for accurate satellite tracking.
Some GNSS antennas also use notch filters. These filters block known interference sources, such as LTE or Wi-Fi signals. Designers can customize these filters based on expected electromagnetic environments. Moreover, filters inside the antenna reduce the need for external filtering components. This integration simplifies system design and improves electromagnetic compatibility. It also ensures consistent performance across various installations.
Temperature stability is important for filter performance. High-quality GNSS antennas use filters with stable characteristics over a wide temperature range. This helps maintain signal integrity in harsh conditions.
In multi-constellation receivers, filters must support several frequency bands. Modern antennas include multi-band filtering to handle GPS, Galileo, GLONASS, and BeiDou signals simultaneously.
In conclusion, built-in filters are critical for GNSS antenna performance. They block interference, protect the receiver, and improve positioning accuracy. With growing signal congestion, well-designed filtering is more important than ever in modern GNSS systems.
Built-in filters